In 2025, device authentication will be transformed by biometric methods, enhancing security and reducing reliance on traditional passwords. Multi-factor authentication will integrate knowledge, possession, and biometrics for robust protection. AI-powered solutions will analyze user behaviors, swiftly detecting anomalies. Blockchain technology will introduce decentralized identities, improving trust and automating processes. Organizations must also adapt to quantum computing threats, focusing on post-quantum cryptography. This evolving landscape promises better security and user experience, with more advancements on the horizon.
Key Takeaways
- Implement biometric authentication to enhance security and user experience by eliminating traditional passwords and reducing phishing risks. Utilize multi-factor authentication (MFA) to combine various verification methods, ensuring robust protection against unauthorized access. Adopt AI-powered authentication solutions to analyze user behavior and swiftly detect anomalies, minimizing risks of data breaches. Explore blockchain technology for decentralized and tamper-proof identity verification, enhancing trust and automating authentication processes. Prioritize post-quantum cryptography to safeguard sensitive data against future quantum computing threats, ensuring resilient authentication frameworks.
The Rise of Biometric Authentication
As technology advances, the adoption of biometric authentication has surged, transforming the landscape of device security. This innovative approach leverages unique biological traits, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris scans, to authenticate users.
Organizations increasingly favor biometrics due to its efficiency and enhanced security features, minimizing reliance on traditional passwords that are often vulnerable to breaches. The integration of biometric systems into smartphones, laptops, and security devices has made access more seamless, reducing friction for users while ensuring robust protection.
Privacy concerns, however, accompany this rise, as individuals grapple with the storage and management of their biometric data. Overall, the trend signifies a shift towards more secure, user-friendly authentication methods, reflecting the growing importance of safeguarding sensitive information in a digital world.
Enhancing Security With Multi-Factor Authentication
How can organizations bolster their security measures against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats? One effective strategy is the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a system, considerably enhancing security.
This method combines something the user knows, like a password, with something they have, such as a smartphone or hardware token, and sometimes even something they are, like a biometric identifier. By employing MFA, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with stolen credentials and unauthorized access.
As cybercriminals continue to develop advanced techniques, adopting MFA not only secures sensitive data but also fosters user trust and compliance with regulatory requirements. This makes it an essential component of contemporary cybersecurity frameworks.
AI-Powered Authentication Solutions
While traditional authentication methods have proven effective, the emergence of AI-powered authentication solutions represents a significant advancement in cybersecurity.
These solutions leverage machine learning algorithms to analyze user behavior patterns, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of identity verification processes.

By continuously adapting to evolving threats, AI can detect anomalies that may indicate unauthorized access more swiftly than conventional methods.
In addition, AI-powered systems can integrate biometrics, such as facial recognition or voice authentication, adding an additional layer of security.
This proactive approach not only streamlines user experiences but also minimizes the risk of data breaches.
As organizations increasingly adopt these advanced technologies, AI-powered authentication solutions are set to redefine the landscape of secure access in 2025 and beyond.
The Role of Blockchain in Device Security
AI-powered authentication solutions enhance cybersecurity by analyzing user behavior and integrating biometrics. In this evolving landscape, blockchain technology emerges as a pivotal force in device security.
By providing a decentralized ledger, blockchain guarantees that device identities are immutable and tamper-proof. Each device can be registered on the blockchain, creating a unique, verifiable identity that enhances trust among users and systems.
Blockchain technology ensures device identities are immutable and tamper-proof, fostering trust through unique, verifiable registrations.
Additionally, smart contracts automate the authentication process, enabling real-time verification without intermediaries. This reduces the risk of identity theft and unauthorized access while increasing transparency.
As organizations increasingly adopt blockchain, the potential for a more secure and resilient authentication framework becomes apparent, paving the way for a future where device security is both robust and efficient.
Zero Trust Architecture: A New Paradigm
As organizations face increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, the adoption of Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) has emerged as an essential strategy in enhancing device security.
Unlike traditional security models that assume trust within the network perimeter, ZTA operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify." This framework requires continuous authentication, limiting access to resources based on strict identity verification.
By segmenting networks and enforcing least privilege access, ZTA minimizes potential attack surfaces. In addition, ZTA accommodates the growing prevalence of remote work and cloud services, ensuring that every device and user is scrutinized, regardless of location.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, ZTA represents a proactive approach, reinforcing organizational resilience and safeguarding sensitive data against unauthorized access.
Behavioral Biometrics: Identifying Users by Their Actions
In the context of Zero Trust Architecture, behavioral biometrics has emerged as a powerful tool for enhancing user authentication. This technology analyzes unique patterns in user behavior, creating a dynamic profile that https://aquipress.com/top-rated-pki-management-platform-unveiled/ evolves with each interaction.
By focusing on how users engage with their devices, organizations can better secure sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
Key elements of behavioral biometrics include:
Keystroke Dynamics: Monitoring typing speed and patterns. Mouse Movements: Analyzing the way users navigate interfaces. Touch Gestures: Evaluating swiping and tapping behavior on touchscreens. Location Tracking: appraising where users typically access devices.These insights not only strengthen security but also facilitate seamless user experiences in an increasingly digital landscape.
Passwordless Authentication: The Future of Secure Access
While traditional passwords have long been the cornerstone of digital security, the rise of passwordless authentication is redefining how users access their accounts. This innovative approach leverages biometric data, hardware tokens, and one-time codes to eliminate the need for passwords.
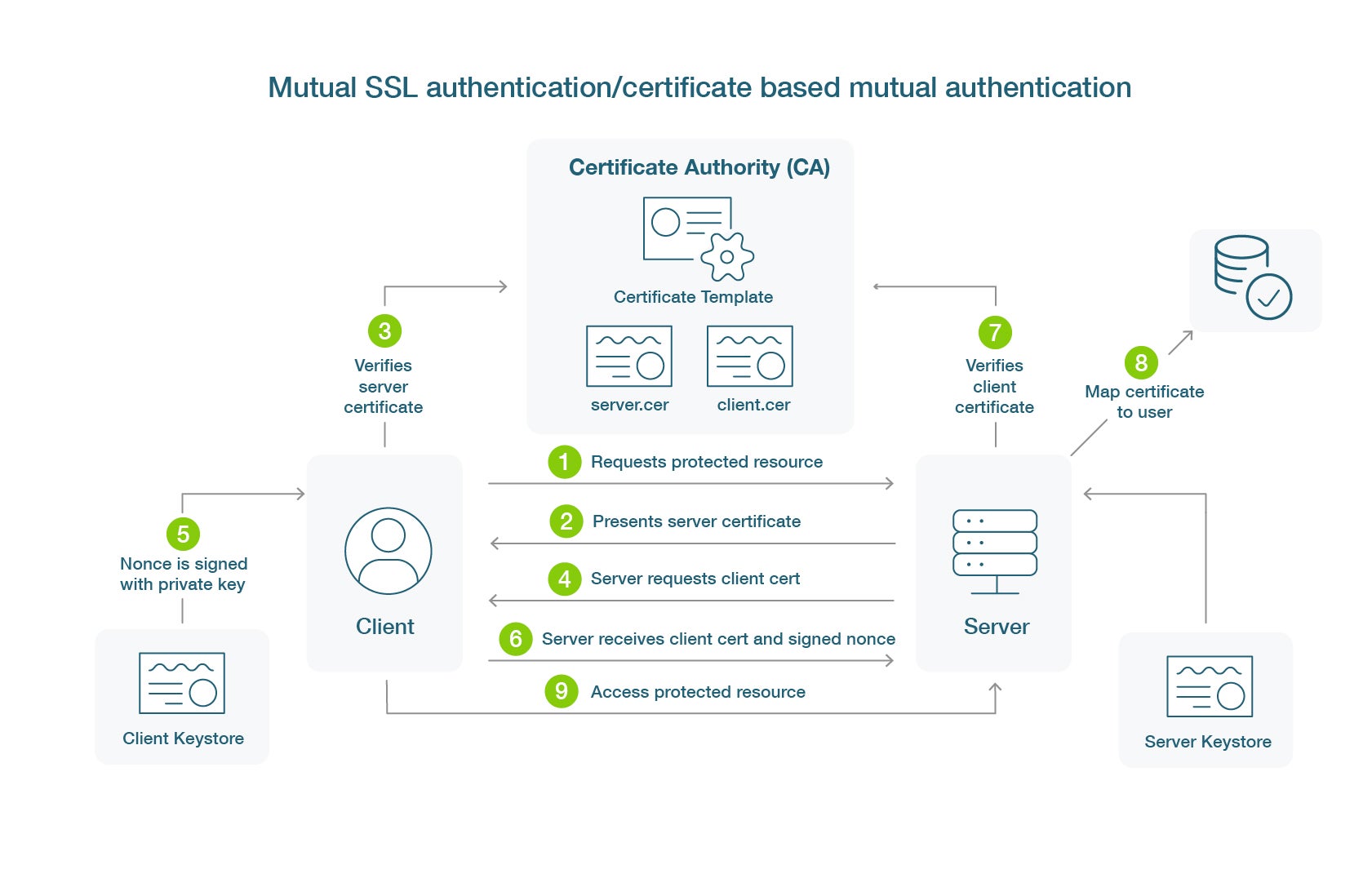
By utilizing methods such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, organizations enhance security while improving user experience. Passwordless authentication reduces the risk of phishing attacks and credential theft, as there are no static passwords to compromise.
As more businesses adopt this technology, the emphasis on convenience and security will drive widespread acceptance. Ultimately, passwordless authentication represents a significant shift towards a more secure, user-friendly digital landscape, fostering trust and confidence in online interactions.
Secure Identity Verification Through Decentralization
With the increasing demand for secure identity verification, decentralization has emerged as a transformative solution. This approach empowers individuals by granting them control over their personal data, minimizing risks associated with centralized systems.
Decentralization redefines identity verification, empowering individuals with control over their personal data and enhancing security.
Decentralized identity verification can enhance security and privacy through several key features:
Self-sovereign Identity: Users own and manage their identities without relying on third parties. Immutable Records: Transactions and verifications are securely recorded on blockchain, ensuring transparency and trust. Reduced Fraud: The decentralized nature makes it considerably harder for malicious actors to manipulate identities. Interoperability: Decentralized systems can seamlessly interact across various platforms, fostering broader acceptance and usability.The Impact of Quantum Computing on Authentication Methods
Quantum computing presents a significant threat to traditional encryption methods, potentially compromising the security of existing authentication systems.
As a response, researchers are exploring post-quantum cryptography solutions to safeguard against these emerging vulnerabilities.
Enhancing security protocols in light of quantum advancements will be essential for maintaining robust device authentication in the future.
Quantum Threat to Encryption
How might the advent of quantum computing reshape the landscape of digital security? As quantum computers advance, they pose significant threats to traditional encryption methods, potentially undermining the very foundations of secure communication.
The impact can be summarized through key vulnerabilities:
Public Key Cryptography: Quantum algorithms can easily break RSA and ECC, rendering them ineffective. Data Breaches: Sensitive data encrypted today could be decrypted in the future, leading to long-term exposure. Authentication Protocols: Quantum capabilities may bypass conventional authentication methods, increasing fraud risk. Integrity Risks: The ability to manipulate encrypted data without detection threatens the integrity of digital transactions.In this evolving landscape, awareness of quantum threats is vital for enhancing device authentication and safeguarding digital assets.
Post-Quantum Cryptography Solutions
As the threat of quantum computing looms, the development of post-quantum cryptography solutions becomes increasingly crucial for securing authentication methods.
Traditional cryptographic algorithms, such as RSA and ECC, are vulnerable to quantum attacks, necessitating a shift to quantum-resistant alternatives. Researchers are exploring lattice-based, hash-based, and code-based cryptographic techniques that promise heightened security against quantum threats.
These solutions aim to guarantee that authentication processes remain robust, safeguarding sensitive data and user identities. As organizations begin to adopt these technologies, the focus will shift from merely implementing existing standards to developing new frameworks that integrate post-quantum principles.
This proactive approach will be essential to maintain trust and security in an increasingly digital and quantum-computing-capable world.
Enhancing Security Protocols
While the emergence of quantum computing presents significant challenges, it also necessitates a reevaluation of existing security protocols in authentication methods. As traditional encryption methods become vulnerable, organizations must adopt enhanced security measures.
Key strategies include:
Quantum-resistant algorithms: Implement new cryptographic techniques that can withstand quantum attacks. Multi-factor authentication: Strengthen access controls through additional verification methods, such as biometric data or one-time codes. Regular protocol updates: Continuously assess and upgrade security measures to counter evolving threats. User education: Increase awareness and training for users on secure practices to mitigate human error.These strategies aim to bolster authentication systems, ensuring resilience against the impending quantum revolution and safeguarding sensitive information.
User Experience: Balancing Security and Convenience
Ensuring a seamless user experience in device authentication requires a careful balance between security measures and convenience. Users demand quick and efficient access to their devices while also expecting robust protection against unauthorized access.
Overly stringent security protocols can lead to frustration, prompting users to seek shortcuts that ultimately compromise safety. Conversely, lax security can expose devices to vulnerabilities, risking sensitive information.
Innovative solutions, such as biometric authentication and adaptive security measures, are emerging to bridge this gap. These technologies offer strong security while minimizing user friction.
As organizations prioritize user experience in their authentication strategies, they must remain vigilant in safeguarding against evolving threats, ensuring that security enhancements do not detract from overall usability.
FAQ
What Are the Costs Associated With Implementing Advanced Authentication Technologies?
The costs associated with implementing advanced authentication technologies can vary greatly based on several factors.
Organizations may incur expenses related to software development, hardware upgrades, and ongoing maintenance.
Additionally, training staff to effectively use these technologies can contribute to overall costs.
Security assessments and compliance with regulatory requirements may further increase financial burdens.
Ultimately, the initial investment may be substantial, but organizations often weigh these costs against potential security benefits and risk mitigation.
How Can Organizations Ensure User Privacy With Biometric Data?
Organizations can guarantee user privacy with biometric data by implementing strong encryption protocols and secure storage solutions.
They should also adopt privacy-by-design principles, minimizing data collection and processing only what is necessary. Regular audits and compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR, are essential.
Additionally, educating users about their rights and the importance of biometric security can foster trust and transparency, ultimately enhancing the overall security framework of the organization.
What Are the Potential Risks of Relying on AI for Authentication?
Relying on AI for authentication introduces several potential risks.

To begin with, algorithms may be vulnerable to bias, leading to unequal access for certain user groups.
Additionally, sophisticated attacks, such as adversarial machine learning, can manipulate AI systems, compromising security.
Moreover, over-reliance on AI could result in reduced human oversight, increasing the likelihood of undetected breaches.
Finally, privacy concerns arise if sensitive data used for training AI is inadequately protected or mismanaged.
How Does the Adoption of New Authentication Methods Impact Legacy Systems?
As a bridge spanning a turbulent river, the adoption of new authentication methods connects modern technology with legacy systems.
This integration often presents challenges, as older systems may struggle to support advanced protocols, leading to potential vulnerabilities.
The clash of innovation and tradition symbolizes the friction between efficiency and security.
Consequently, organizations must navigate these waters carefully, ensuring that legacy systems evolve alongside new techniques to maintain a robust security posture.
What Regulations Govern Biometric and Authentication Technologies?
Regulations governing biometric and authentication technologies typically focus on privacy, data protection, and security.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe sets stringent requirements for the handling of personal data, including biometric information.
In the United States, various state laws, such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), impose obligations on companies regarding data collection and user consent.
Compliance with these regulations is vital for organizations utilizing biometric technologies to guarantee ethical practices and user trust.
Conclusion
As the digital landscape evolves, the future of device authentication in 2025 promises to be a symphony of innovative technologies harmonizing security and user experience. From biometric advancements to blockchain's decentralized fortresses, the multifaceted approaches will create a robust shield against cyber threats. Embracing passwordless solutions and zero trust principles will not only enhance security but also guarantee seamless access for users. In this brave new world, effective authentication will be the key that opens a safer digital domain.